ActiveMQ vs RabbitMQ vs Kafka
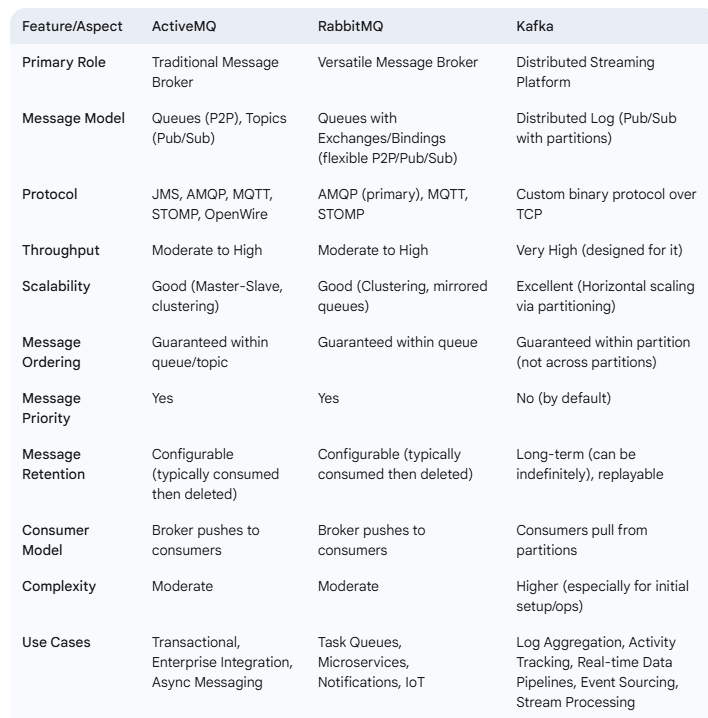
When to Use:
- ActiveMQ: Best suited for traditional enterprise systems, legacy JMS-based applications, and use cases requiring multiple protocol support.
- RabbitMQ: Ideal for modern cloud-native applications, microservices, real-time messaging, and scenarios requiring high throughput.
- Kafka: Designed for event-driven architectures, big data pipelines, real-time analytics, and scenarios requiring extremely high throughput and durability.
RabbitMQ is not popular anymore, we usually choose Kafka for large systems or choose a queue within cloud we use like Google pub/sub if you're using GCP (Google Cloud Platform) or Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS).
Today we will learn about rabbitMQ to know basis about how a queue works
- Producer (Provider Service)
- Sends messages to an exchange in RabbitMQ.
- Uses
direct,topic,fanout, orheadersexchanges depending on routing needs.
- Broker (RabbitMQ Server)
- Routes messages to
queuesbased on exchange type.
- Routes messages to
- Consumer (Public Subscriber)
- Listens to
queuesand processes messages.
- Listens to
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>docker-compose.yml
services:
rabbitmq:
image: rabbitmq:3.12-management # Includes the web management UI
container_name: rabbitmq
restart: always
environment:
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER: admin
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS: admin
ports:
- "5672:5672" # AMQP protocol port
- "15672:15672" # Management UI port
volumes:
- rabbitmq_data:/var/lib/rabbitmq # Persist RabbitMQ data
volumes:
rabbitmq_data:
driver: localdocker-compose up -dIn order to access web, using port 15672, http://localhost:15672
RabbitMQ Exchange types
RabbitMQ supports four main types of exchanges: Direct, Fanout, Topic, and Headers.
Exchange Type && When to Use
- Direct: Specific routing based on exact keys.
- Fanout: Broadcast to multiple consumers.
- Topic: Pattern-based routing (e.g., logs, multi-level keys).
- Headers: Advanced routing with custom attributes.
1. Direct Exchange (direct)
Routes messages to queues with an exact matching routing key
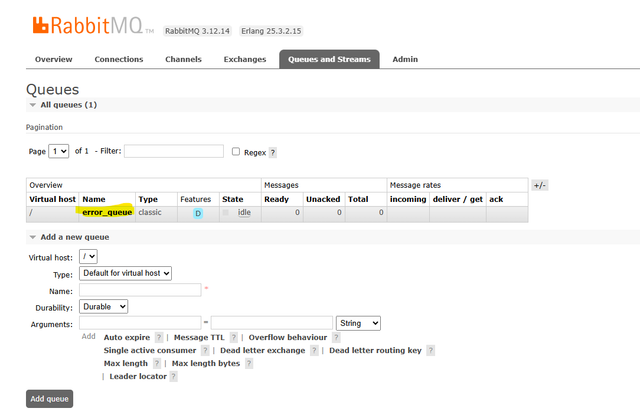
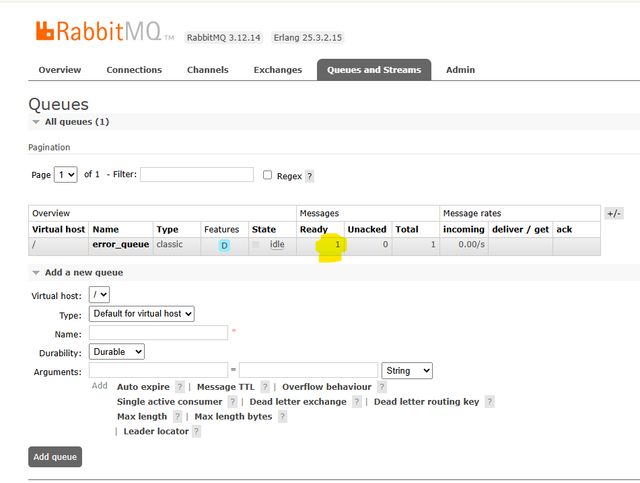
- Create a new queue: error_queue
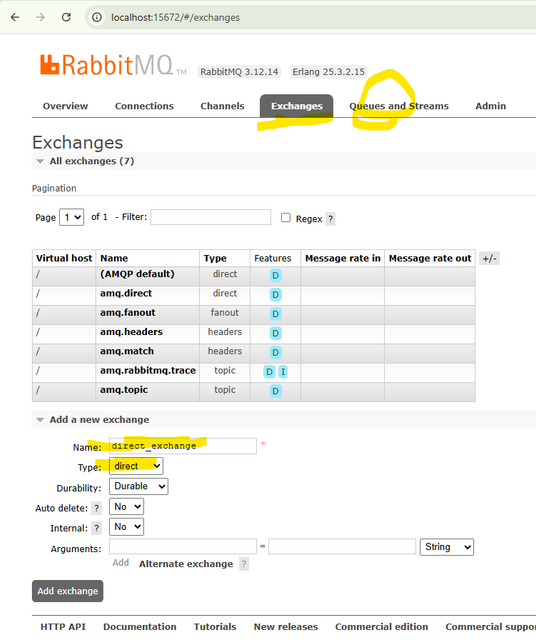
- Create a new
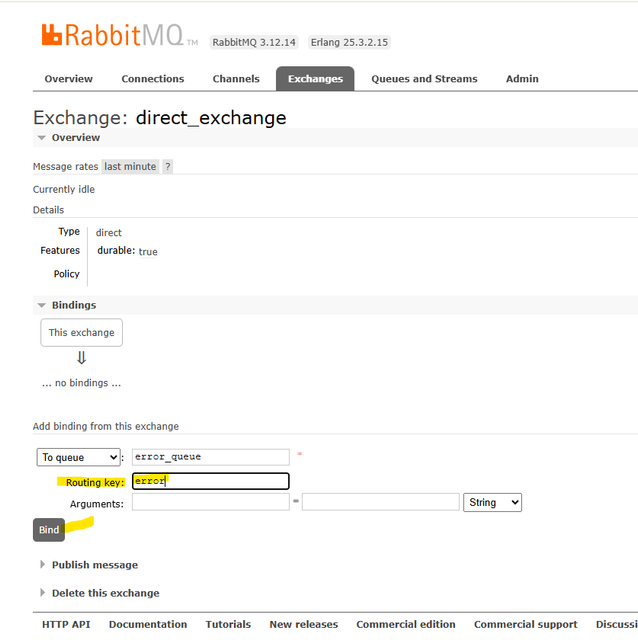
directexchange: direct_exchange - In
direct_exchange, add binding toerror_queuewithrouting key:error - Write code to send message to
direct_exchange - Write code to receive message from
error_queuequeue
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "error_queue";
public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_exchange";
public static final String ROUTING_KEY = "error";
}import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MessageProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.EXCHANGE_NAME, RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY, message);
}
}
2. Fanout Exchange (fanout)
Broadcasts messages to all bound queues, ignoring routing keys.
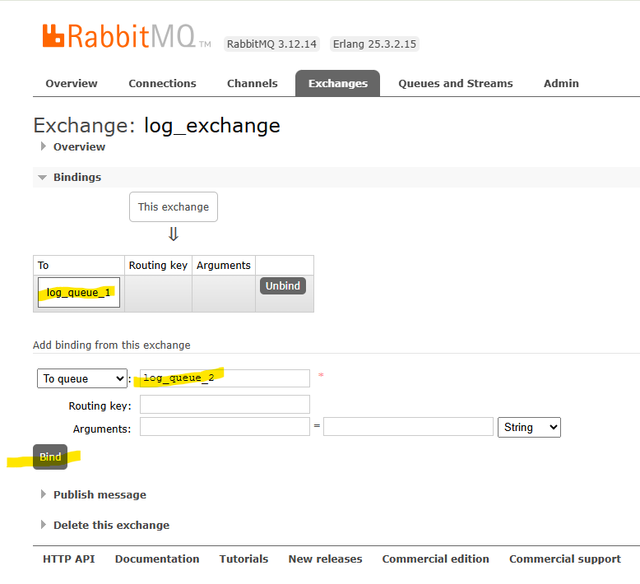
- Create 2 new queues:
log_queue_1,log_queue_2 - Create a new
fanoutexchange:log_exchange - In
log_exchange, add binding tolog_queue_1,log_queue_2 - Write code to send message to
log_exchange - Write code to receive message from
log_queue_1andlog_queue_2queues
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("log_exchange", "", message);
3. Topic Exchange (topic)
Routes messages based on pattern matching in routing keys using:
*→ Matches one word.#→ Matches multiple words.
Create 2 queues: app1_logs, app2_log
Create topic exchange: logs_topic
In logs_topic, create 2 binding to 2 queues
- binding 1:
- to queue:
app1_log - routing key:
logs.error.app1
- to queue:
- binding 2:
- to queue:
app2_log - routing key:
logs.info.app2
- to queue:
Send message to logs_topic with routing key: logs.*.app1
Only app1_log queue receive message.
4. Headers Exchange (headers)
Uses message headers (instead of routing keys) for routing.
- Create a queue:
pdf_logs - Create header exchange:
logs_headers- format = pdf
- Send message to
logs_headerswith headers:{format: "pdf", type: "report" }

public void sendHeadersMessage() {
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
messageProperties.setHeader("format", "pdf");
messageProperties.setHeader("type", "report");
Message msg = new Message("Here is a headers message".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), messageProperties);
rabbitTemplate.send("logs_headers", "", msg); // Headers exchange ignores routing keys
}